It can be very handy sometimes to tunnel your browser’s traffic through a secure channel, for example when you are on an insecure or unknown network like a hotel, cafe or airport etc.
To open up a SOCKS proxy on port 8080, run
ssh -C2qTnN -D 8080 your-user@example.com
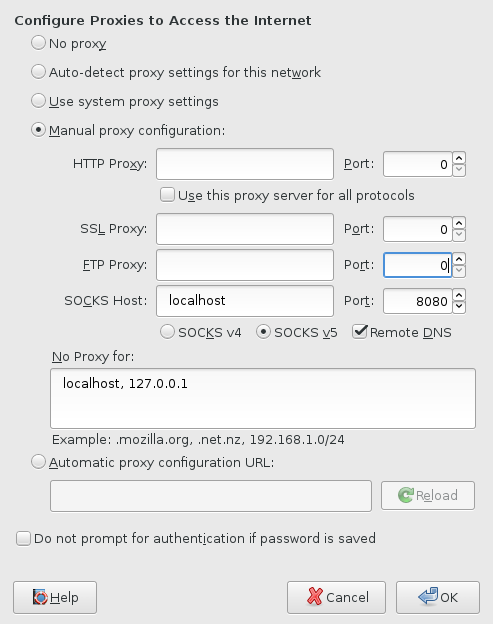
To configure Firefox to use the proxy go to Edit → Preferences → Advanced → Network → Settings and enable ‘Manual proxy configuration’
You can also tunnel Firefox’s DNS queries through the SOCKS proxy by enabling the ‘Remote DNS’ checkbox.
For chrome, you can use the settings dialog quite similar to the Firefox example above, but you can also specify the proxy through the command line with the SOCKS_SERVER environment variable. To spawn a new, temporary chrome session with the SOCKS proxy configured, run
SOCKS_SERVER=localhost:8080 google-chrome --user-data-dir=/tmp/chrome $1
Note that’s it’s a bit more tricky to tell chrome not to rely on local DNS queries. For details have a look at the chromium documentation.
Resources:
https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=1536126